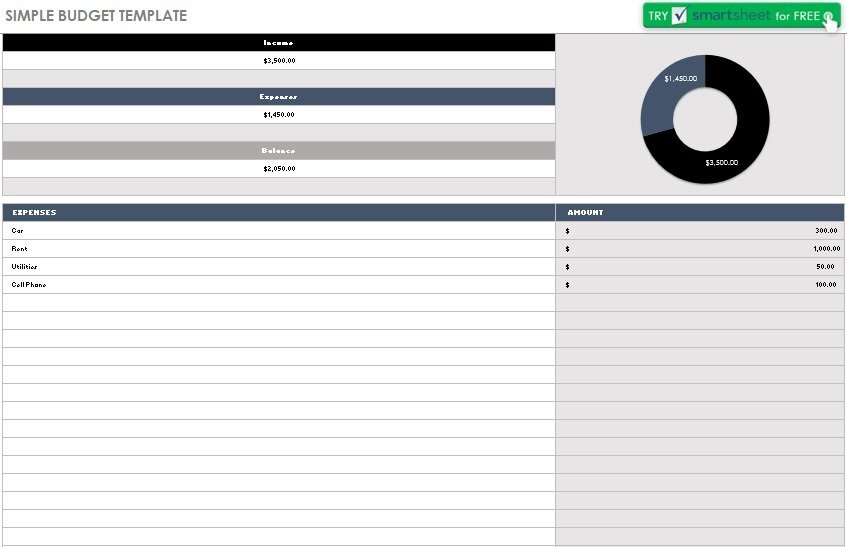
Smooth out how you spending personal monthly budget template your pay with this extensive planning format. With an individual spending plan format, the financial plan of the board is so natural. Succeed crunches the numbers so you can focus on your funds. This personal monthly budget template thinks about the project and real pay and anticipated and genuine costs. It incorporates a variety of classifications and subcategories, so you can set it up precisely how you’d like. Use this month-to-month financial plan worksheet to put together and plan your budgets. Whenever you’re not in the workplace, this financial plan format serves as a printable spending plan worksheet you can take in a hurry. This is an open format.
What is a Personal Monthly Budget?
An arrangement that classifies and dispenses pay towards costs, reserve funds, and obligations. Monitoring pay and costs are a prerequisite in many families to bring in certain cash extend from one check to another. While spending plans are great for everybody, assuming you’re one of numerous that are observing that your monetary circumstance is in difficult circumstances in light of a financial downturn or an adjustment of your business, this is the ideal chance to begin a month-to-month financial plan and deal with your funds. Making a financial plan can provide you with the inner harmony that things will be good over the long haul, regardless of the ongoing conditions. Above an arrangement, a spending plan is likewise an organized rundown. Seeing your costs spread out in a financial plan assists you with finding and characterizing spending designs, overspending, overflows, and getting an exact image of your spending. Posting all of your pay for a month against the entirety of your spending, either for required or optional costs, will assist you with seeing your income so you can settle on better choices and comprehend what you can and can’t manage.
Begin with Categorizing
A strong financial plan represents each sort of expenditure you’ll most likely embrace during the month. Inadequate financial plans frequently need more classes, and accordingly, cash just “disappears,” or the classifications are explicit and spending becomes difficult to monitor. Making your month-to-month financial plan represent every need, under a classification like utilities, and each optional buy, under a classification like individual consideration, assists you with dealing with your spending.
Spending plan Categories
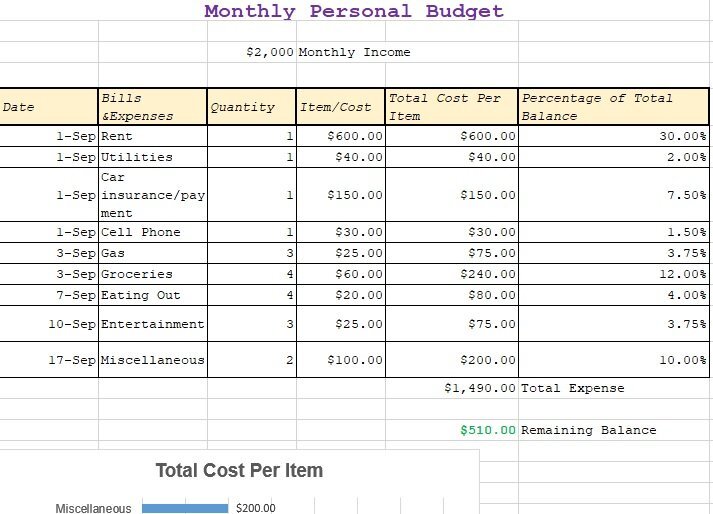
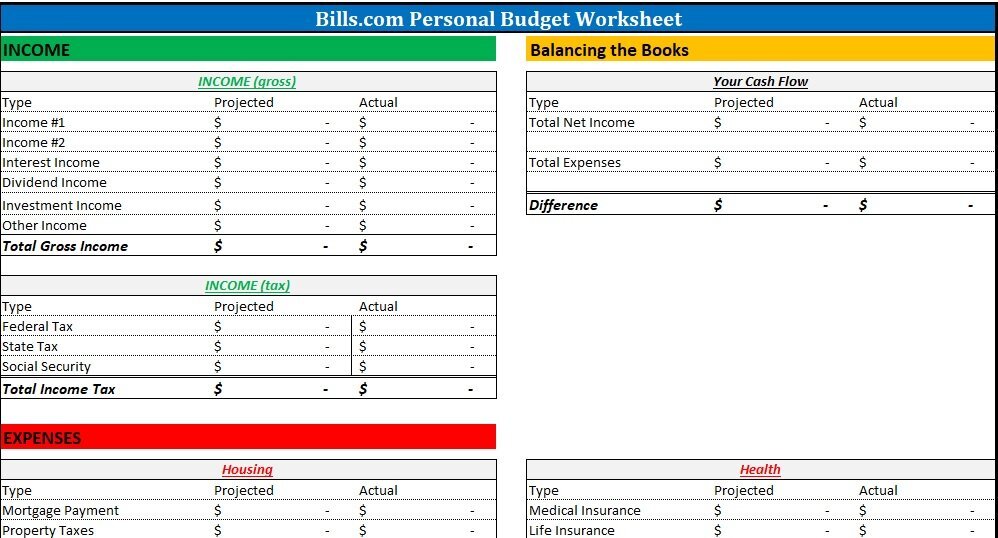
Spending plan Categories, when appropriately carried out, assist you with accomplishing your monetary objectives. For instance, assuming you lay out the objective toward the start of the month, “I need to spend just 100 dollars on amusement,” then you can without much of a stretch dispense cash for motion pictures and games and not spend over that sum. The spending plan class in this situation is, “amusement.” The classifications recorded beneath will cover practically the entirety of your monetary requirements over time, however, these classifications are intended to be customized to your way of life, so go ahead and add or remove classes as you see fit. Lease/contract – Money from this classification keeps the rooftop over your head. Utilities – Bills like water, gas, power, sewer, waste, and reuse. Telephone/Internet – Amounts in this classification might be variable assuming you frequently go over information cutoff points or pay on a “pay for what you use” plan. Car – Car installments, specifying, and support. If you don’t possess a vehicle, this could be the expense of transportation. Food/food – For some, it could be smart to part this classification into two, one for your at-home food, and one more for eating out. Whether you incorporate non-food things like cleanser and bathroom tissue in this class depends on you. Diversion – Movies, books, games, and entertainment. Investment funds – Money that isn’t to be spent however saved for your monetary objectives. An investment fund of 90 days of your pay is a protected air pocket to hold back nothing the most terrible occurs, and you want to live off your reserve funds. Clinical/medical care – check-ups, arrangements, medication. Protection – Car protection and medical coverage. Training – Current semester installments, books, and supplies, lodging, expenses for excursions or memberships, or coaches. Clothing – As a fundamental however frequently costly thing, a dress may not be a month-to-month cost for all, but rather perhaps every other month or semiannual cost. Individual Care – Taking consideration of yourself appears to be unique for each family, yet this class could incorporate costs like rec centre enrollments, salon visits, beauty care products, or keeping an eye on you want a night out. Obligation – This class might be permanently established, for example, assuming you’re taking care of a vehicle, house, or advance, or it could be steadily changing, for example, if you’re gathering different Visa sums every month. It is vital for spending to plan this cash to stay away from FICO rating plunges or pay garnishment. Gifts – For some, altruistic gifts are a normal cost, for example, chapel tithes. If they’re not, and you might want to turn into a customary ally of an association, concluding this could be a satisfying expansion to your costs.
The most effective method to Make a Personal Monthly Budget
Before having the option to define monetary objectives, you should have thought about what you’re right now making and spending. Going through the accompanying advances will assist you with laying out a benchmark of pay as opposed to spending, ideally laying out that you have an excess and not a shortfall, and assist you with making a monetary objective, such as reducing amusement expenses, expanding gifts, or multiplying your investment funds.
Assemble your monetary administrative work
Whether through your web-based entrances or the mail, you’ll have to lay out your ongoing bills and types of revenue, and this will come as your monetary administrative work. This administrative work could incorporate bank proclamations, venture accounts, service bills, pay nails, W-2s or 1099s, Mastercard bills, staple or attire receipts, lease receipts or home loan articulations, and everyday life advance explanations.
Calculate your income
A paycheck may arrive once a month, twice a month, or even weekly, depending on your profession. If you’re independently employed or dependent on government checks, any cash you take in ought to be incorporated. Record the aggregate sum for the month in this classification. To establish your baseline, you should use your bank statements and pay stubs.
Create a list of monthly expenses
Utilizing your administrative work, layout the essential and repeating costs for your spending plan. A bank statement, utility bill, credit card bill, grocery receipt, housing cost, and loan information could be included. Keep an eye on things like subscriptions, which can easily be overlooked, but can add up over time.
Decide fixed and variable costs
Fixed costs don’t change from one month to another. You know the very thing you hope to pay each time. Variable costs are yet to be determined. These could be birthday presents, gas, Visa adjustments, power bills, and so on. Investigate your administrative work to decide the best guess or a normal for your variable costs.
Absolute your pay and costs
With all the data you’ve previously accumulated, decide the amount of all your month-to-month pay and all your month-to-month expenses. Assuming that you’re getting more cash than you’re spending, you’re looking great so far. On the off chance that you’re spending more cash than you’re making, you’ll have to make changes in the subsequent stage.
Make changes following costs
Here you put forth a monetary objective (spend less, save more, take care of obligation). Assuming you find toward the finish of the past advance that you’re bleeding cash, don’t surrender. You might want to offer up, yet you have a chance to fix the issue before you’re in too far. As you make changes, you’ll have to give close consideration to where you’re spending and see where you can scale back. As you glance through your receipts and bank explanations, pose yourself these inquiries:
- Is this thing or administration a need?/Do I want it?
- How might I chop this cost down without killing it completely? Could I at any point observe a lower rate or haggle at a lower cost?
- Is it conceivable to cut this expense? Assuming this is the case, I can add it back when my cash is in better shape.
On the off chance that you’re reluctant to cut your costs, investigate ways of cutting customary installments like vehicle protection. Look closely, and you could observe a lower rate through another organization. The focus on the finish of the change stage relies upon the sort of spending plan. If you have any desire to have a reasonable financial plan, the objective isn’t to have an excess; it’s to have your pay and costs equivalent.
free personal monthly budget template
printable personal monthly budget template
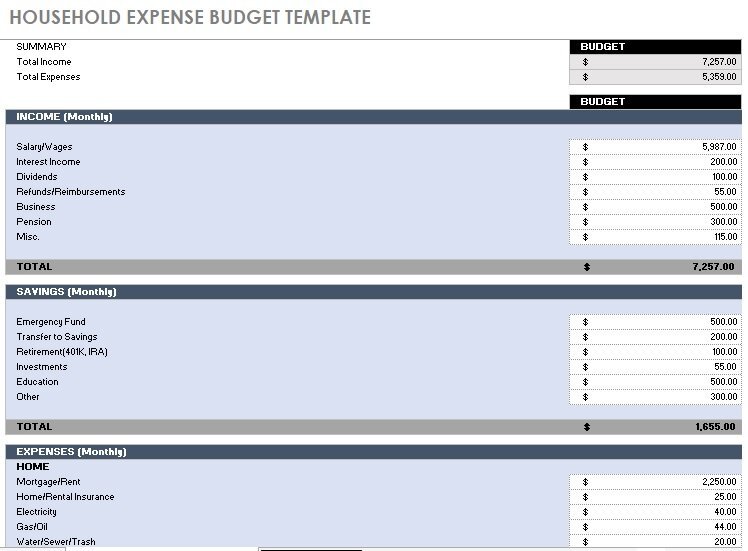
monthly household budget template
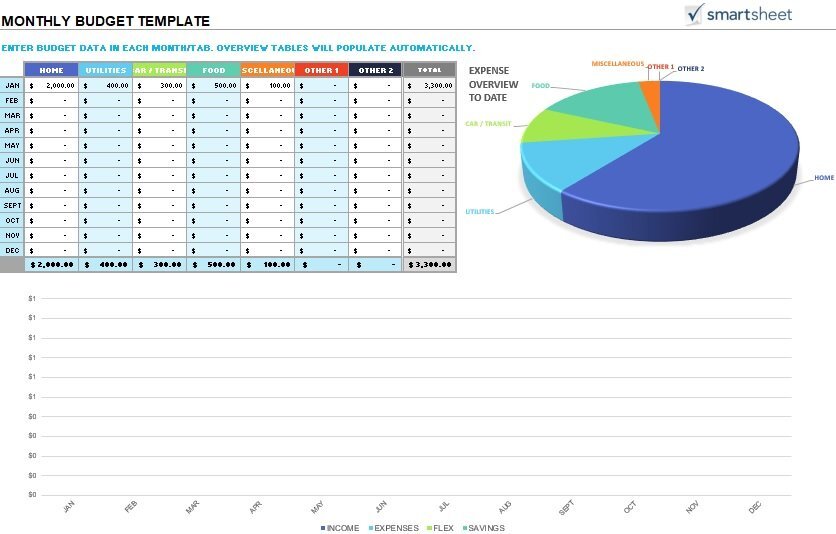
personal monthly budget template with graphs
printable personal monthly budget template 1
free personal monthly budget template excel
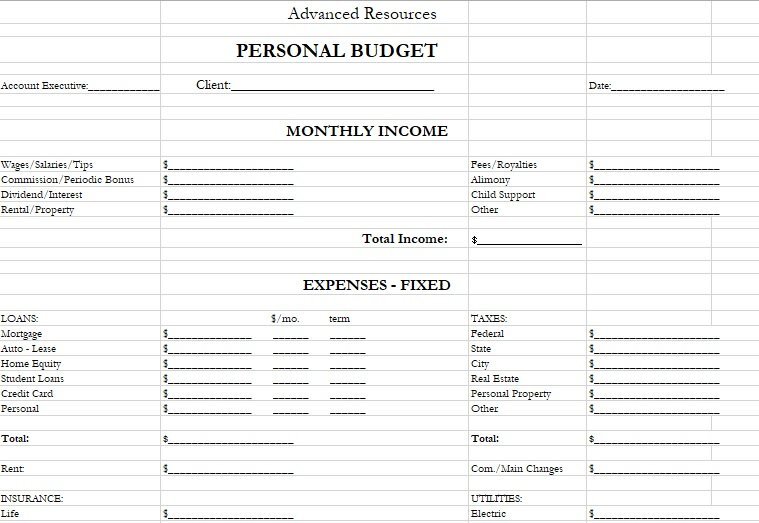
best personal monthly budget template
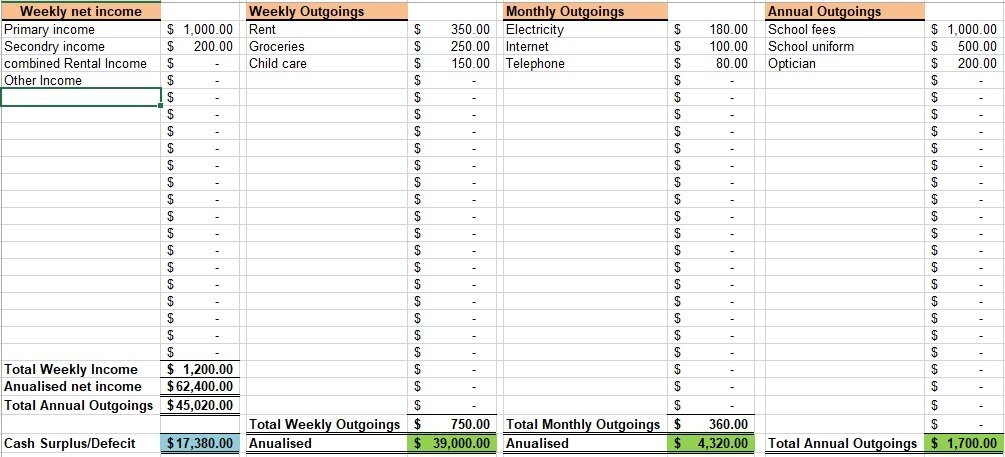
free personal monthly budget spreadsheet
Conclusion
A good personal monthly budget template should follow the 50/30/20 rule. According to this method, your monthly take-home income is divided into three categories: 50% for needs, 30% for wants and 20% for savings and debt repayment. Whenever you pay yourself first, you pay yourself (for the most part through programmed investment funds) before you do some other spending. As such, you are focusing on your drawn-out monetary prosperity.
What ought to be in an individual month-to-month spending plan?
Essential Monthly Expenses Eateries and Groceries. While planning for your month-to-month expenses, begin with what we call the Four Walls-otherwise is known as the necessities you want to make due: food, utilities, asylum, and transportation. …
- Utilities. …
- Lodging. …
- Transportation. …
- Giving. …
- Protection. …
- Fundamentals. …
- Childcare.
How would I make a month-to-month private financial plan?
- Stage 1: Calculate your overall gain. The groundwork of a powerful spending plan is your net gain. …
- Next Stage 2: Track your spending. …
- Moreover Stage 3: Set reasonable objectives. …
- Then Stage 4: Make an arrangement. …
- Further Stage 5: Adjust your spending to remain on a financial plan. …
- Finally Stage 6: Review your spending plan consistently.
What is a decent private spending plan?
Attempt a straightforward planning plan. We suggest the famous 50/30/20 financial plan to expand your cash. In it, you spend generally half of your after-charge dollars on necessities, something like 30% on needs, and somewhere around 20% on investment funds and obligation reimbursement.
What is the 50 30 20 spending plan rule?
The essential guideline is to separate your month to month after-charge pay into three spending classes: Moreover, half for needs, 30% for needs and 20% for reserve funds or taking care of obligations. By consistently keeping your costs adjusted across these primary spending regions, you can give your cash something to do all the more productively.
How could a fledgling financial plan?
Follow the means underneath as you set up your own, customized spending plan:
- Make a rundown of your qualities. Record what makes a difference to you and afterward set up your qualities.
- Moreover, Put forth your objectives.
- Decide your pay. …
- Further, Decide your costs. …
- Likewise, make your spending plan. …
- Further, pay yourself first! …
- Be cautious with charge cards. …
- As a result, inquire intermittently.
What is the 30 rule?
Try not to spend more than 30% of your gross month-to-month pay (your pay before charges and different derivations) on lodging. Assuming you have 70% or more extra, you’re bound to have sufficient cash for your different costs.
What are the 4 straightforward standards for planning?
What are YNAB’s Four Rules?
- Give Every Dollar a Job.
- Embrace Your True Expenses.
- Adapt to any Challenges.
- Age Your Money.





![Free Christmas Budget Templates [Excel] free christmas budget template 1](https://cdn-ildebcd.nitrocdn.com/jnQCRkBozueuJprueOUxlAYnHGPdsTNY/assets/images/optimized/rev-d7007a4/templatedata.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/free-christmas-budget-template-1-150x150.jpg)